
Developing accessible diagnostic tools to improve urinary tract infection care in low- and middle-income countries
Project title: DOSA point-of-care diagnostic for urinary tract infections in low- and middle-income countries (DOSA3)
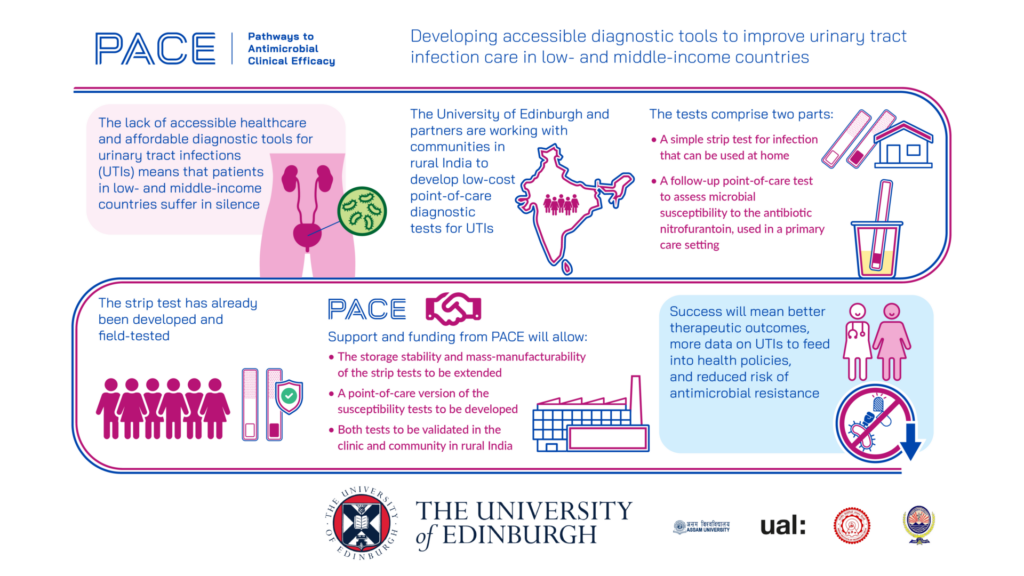
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common infectious diseases, but many people, particularly women in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), cannot access appropriate care. In addition, the lack of rapid and affordable diagnostic tools means that even when treatment is available, antibiotic prescriptions are often made without a definite diagnosis. This contributes towards poor outcomes for patients and drives antimicrobial resistance.
The University of Edinburgh, in partnership with the University of the Arts London, Assam University, Silchar Medical College and the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (IIT Delhi), is focusing on communities in rural India as a representative LMIC setting to develop two low-cost diagnostic tests for UTIs. These can be used in conjunction at the point of care to reduce inappropriate prescribing. The first is a colorimetric paper-based strip test for bacterial infections in urine, which is simple enough to be used in the home by non-specialists. If this gives a positive result, it is followed up in a primary care setting by a second point-of-care test, which is used on a urine sample to rapidly determine the susceptibility of the bacteria to nitrofurantoin, an antibiotic commonly indicated for UTIs.
The project has been phased, initially involving the co-development of the test and user needs, followed by field performance testing to ensure usability, acceptability and effectiveness of the strip tests in overcoming diagnostic challenges specific to LMICs. With funding and support from PACE, the project will increase the storage stability and mass-manufacturability of the strip test, develop the susceptibility test so that it is optimal for point-of-care settings, and assess the performance of both tests in the field.
Success for the project will mean improved access to care, better therapeutic outcomes, and more appropriate use of antibiotics in LMICs, contributing to the fight against antimicrobial resistance. The project will also deliver data that is urgently needed for better policy interventions to tackle UTIs.
University of Edinburgh Summary
The Institute for Regeneration and Repair (IRR) is a research institute based at the University of Edinburgh. Our scientists and clinicians study stem cell biology, inflammation and disease to advance human health and reproductive outcomes.
University of the Arts London Summary
University of the Arts London (UAL) generates and inspires the creativity the world needs for a better future. Since 1842, our Colleges have been defining creative education. With curiosity, imagination and intent, UAL’s community of staff, students and researchers make work that creates lasting change for people and our planet.
UAL is formed of 6 renowned Colleges and 4 Institutes: Camberwell College of Arts, Central Saint Martins, Chelsea College of Arts, London College of Communication, London College of Fashion and Wimbledon College of Arts, AKO Storytelling Institute, UAL Creative Computing Institute, UAL Decolonising Arts Institute and UAL Fashion, Textiles and Technology Institute.
Ranked second globally for Art and Design for the seventh-year running (QS World University Rankings by Subject 2025), UAL delivers world-leading creative education across art, design, fashion, communication, media and performing arts. Our academics and practitioners inspire new ways of thinking through research, innovation and industry collaboration. We work with students enabling them to build the careers of the future because the world needs creativity.
